Introduction
What is the good of a web application without an efficient authentication system?
In this article, I will share how to create a simple and effective authentication for your Django web application.
By default, Django uses the built-in basic authentication system, i.e. (using an email/ username and password to log in directly) how efficient can this be with an Application Programming Interface(API) without tokens for authentication?
Introducing Simple JSON Web Token (JWT) it provides a JSON Web Token authentication backend for a Django REST Framework application.
Let's start building
Create Django Application
Navigate to the directory of your choice on the terminal and create your Django application.
cd desktop # navigated to the desktop directory (windows) django-admin --version # check if django is installed django-admin startproject drf_auth_proj # create django project cd drf_auth_proj # naviage to the project directory django-admin startapp drf_app # create a django applicationCreate a Virtual Environment(optional)
virtualenv venv # created a virtual environment named venv venv\Scripts\activate # activate virtual environment (windows)Install Necessary Dependencies
pip install djangorestframework # install drf(installs django by default) pip install djangorestframework-simplejwt # install simple jwt # add dependencies to requirements.txt file pip freeze > requirements.txt #make sure the virtulal environment is activatedApplication Configuration
We are adding some configurations in the settings.py file(Django app, dependencies).
#settings.py INSTALLED_APPS = [ # add 'drf_app', # django application 'rest_framework', # django rest framework 'rest_framework_simplejwt.token_blacklist', #(JWT BLACKLIST CONFIG) ] # set simple JWT to default authentication REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ( 'rest_framework_simplejwt.authentication.JWTAuthentication', ) }Create a URL file in the application directory(drf_app)
#drf_app/urls.py from django.urls import path from rest_framework_simplejwt.views import ( TokenObtainPairView, TokenRefreshView, ) # import views from JWT urlpatterns = [ #JWT path('token/', TokenObtainPairView.as_view(), name='token_obtain_pair'), path('token/refresh/', TokenRefreshView.as_view(), name='token_refresh'), ]Add the application URL to the project URL file
# drf_auth_proj/urls.py from django.urls import path, include # import include urlpatterns = [ path('api/v1/', include('drf_app.urls')), #add app urls file ]Create customized token-obtain serializer(optional)
This is to add more data/information to a token. The code below adds/encrypts a user's email, and first and last name to the token.
# drf_app/views.py from rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers import TokenObtainPairSerializer class MyTokenObtainPairSerializer(TokenObtainPairSerializer): @classmethod def get_token(cls, user): token = super().get_token(user) # Add custom claims based on your user model fields token['email'] = user.email token['username'] = user.username # token['first_name'] = user.first_name # token['last_name'] = user.last_name return tokenMore JWT configurations
from datetime import timedelta SIMPLE_JWT = { "ACCESS_TOKEN_LIFETIME": timedelta(minutes=5), "REFRESH_TOKEN_LIFETIME": timedelta(days=30), "ROTATE_REFRESH_TOKENS": True, "BLACKLIST_AFTER_ROTATION": True, "UPDATE_LAST_LOGIN": False, "ALGORITHM": "HS256", "VERIFYING_KEY": "", "AUDIENCE": None, "ISSUER": None, "JSON_ENCODER": None, "JWK_URL": None, "LEEWAY": 0, "AUTH_HEADER_TYPES": ("Bearer",), "AUTH_HEADER_NAME": "HTTP_AUTHORIZATION", "USER_ID_FIELD": "id", "USER_ID_CLAIM": "user_id", "USER_AUTHENTICATION_RULE": "rest_framework_simplejwt.authentication.default_user_authentication_rule", "AUTH_TOKEN_CLASSES": ("rest_framework_simplejwt.tokens.AccessToken",), "TOKEN_TYPE_CLAIM": "token_type", "TOKEN_USER_CLASS": "rest_framework_simplejwt.models.TokenUser", "JTI_CLAIM": "jti", "SLIDING_TOKEN_REFRESH_EXP_CLAIM": "refresh_exp", "SLIDING_TOKEN_LIFETIME": timedelta(minutes=5), "SLIDING_TOKEN_REFRESH_LIFETIME": timedelta(days=1), "TOKEN_OBTAIN_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenObtainPairSerializer", "TOKEN_REFRESH_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenRefreshSerializer", "TOKEN_VERIFY_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenVerifySerializer", "TOKEN_BLACKLIST_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenBlacklistSerializer", "SLIDING_TOKEN_OBTAIN_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenObtainSlidingSerializer", "SLIDING_TOKEN_REFRESH_SERIALIZER": "rest_framework_simplejwt.serializers.TokenRefreshSlidingSerializer", "TOKEN_OBTAIN_SERIALIZER": "drf_app.views.MyTokenObtainPairSerializer", }
Migrate the changes to the database
# on the terminal python manage.py migrateCreate Super User
python manage.py createsuperuserCheck the Admin Page (optional)
If you can remember, we did some token blacklist configuration. It saves all tokens generated and makes sure it is used only once.
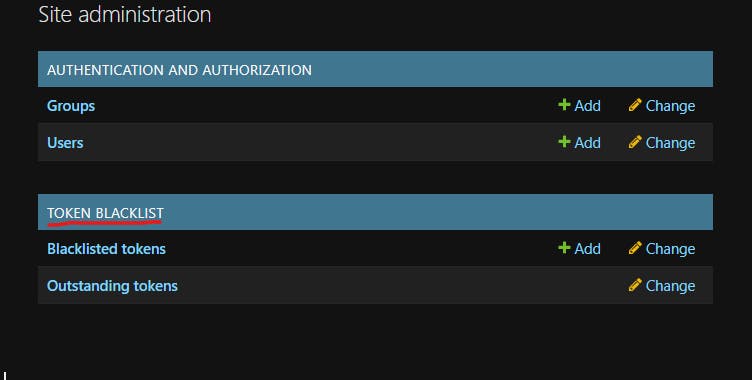
Generate Token
Make sure the server is running
python manage.py runserver. Then, open the Token Obtain Pair URL on a browser and enter the necessary details(username and password).

Decode the Token Generated
Visit the JSON Web Token website https://jwt.io/ and paste any of your tokens there. The email and username field in the image below results from the custom Token Obtain Pair Serializer views.

Here is the link to the project's repository for reference sake.
Conclusion
I hope you found the article helpful and created a JWT authentication for your Django application.
If yes, do well to like and share this piece and comment with me on Linkedin, Twitter and GitHub. And if you like what you read and want to show support, you can buy me coffee😉.